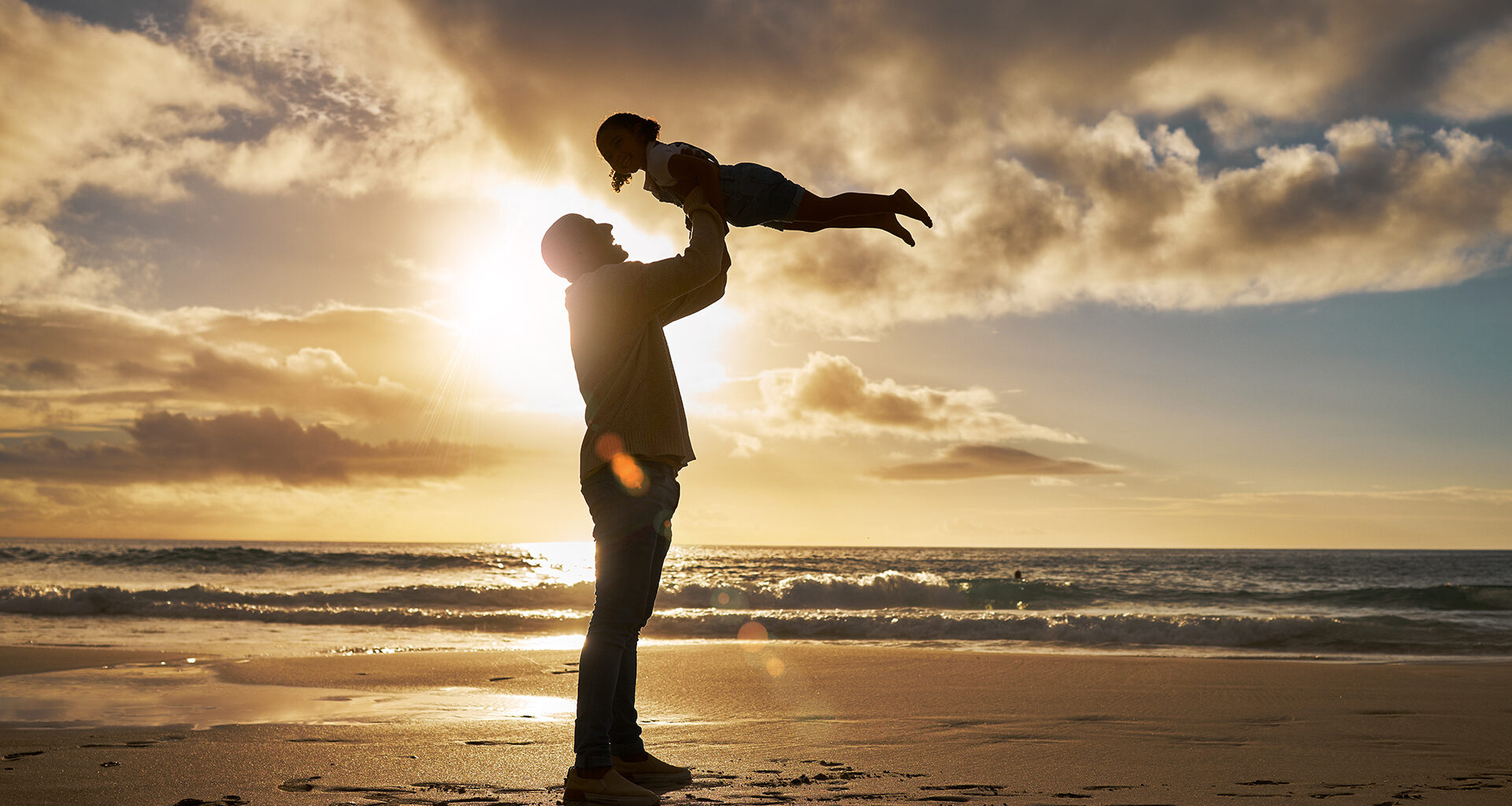
In recent years, a profound shift has occurred in our understanding of well-being and the pursuit of happiness. This shift has been driven by a growing body of scientific research that explores the nature of happiness, its determinants, and its profound impact on the overall quality of life. The “well-being revolution” is not just about feeling good; it’s about understanding the science behind happiness and its potential to transform our lives and society as a whole.
The Pursuit of Happiness:
The pursuit of happiness is a timeless human endeavor. For centuries, philosophers, theologians, and thinkers from various disciplines have contemplated the nature of happiness and how to attain it. However, the study of happiness has traditionally been a philosophical and subjective inquiry, often driven by individual anecdotes and personal reflections.
The Science of Happiness:
In the last few decades, happiness has transitioned from a philosophical concept to a scientific field of study. Researchers in psychology, neuroscience, economics, and other disciplines have embarked on a quest to understand happiness in a systematic and empirical manner. This multidisciplinary approach has yielded remarkable insights into what makes people happy and how happiness can be cultivated.
Key Findings:
The science of happiness has uncovered several key findings:
- Positive Psychology: Positive psychology, a branch of psychology focused on the study of well-being and human strengths, has provided a framework for understanding the factors that contribute to happiness. Researchers have identified elements such as gratitude, resilience, and positive relationships as vital for well-being.
- Hedonic vs. Eudaimonic Happiness: Happiness can be divided into two broad categories: hedonic happiness, which is derived from pleasure and comfort, and eudaimonic happiness, which is linked to purpose, meaning, and personal growth. Both forms of happiness are important for overall well-being.
- Subjective Well-Being (SWB): SWB is a measure of happiness that includes life satisfaction, positive emotions, and a sense of purpose. Researchers have found that factors like income, relationships, and health can influence SWB.
- The Role of Mindfulness and Meditation: Mindfulness practices and meditation have been shown to improve well-being by reducing stress, enhancing emotional regulation, and increasing feelings of gratitude and compassion.
- Social Connection: Positive relationships and social connections are consistently associated with higher levels of happiness. The quality of our social bonds profoundly impacts our overall well-being.
Impact on Quality of Life:
Understanding the science of happiness has far-reaching implications for the quality of life of individuals and societies:
- Health and Longevity: Happiness is linked to better health outcomes and longer life expectancy. Happy individuals tend to engage in healthier behaviors and have stronger immune systems.
- Productivity and Creativity: Happy people are often more productive and creative, leading to enhanced performance at work and in other areas of life.
- Resilience: The ability to bounce back from adversity and cope with life’s challenges is closely related to happiness. Resilient individuals tend to have higher levels of well-being.
- Social Harmony: Societies with higher levels of happiness often exhibit greater social cohesion, trust, and lower levels of crime and conflict.
Cultivating Happiness:
The science of happiness has not only helped us understand happiness but also offers practical strategies for cultivating it. These strategies include practicing gratitude, fostering positive relationships, pursuing meaningful goals, engaging in acts of kindness, and prioritizing self-care.
A Paradigm Shift:
The well-being revolution represents a paradigm shift in how we view happiness and its pursuit. It acknowledges that happiness is not just a fleeting emotional state but a multifaceted and measurable aspect of our lives. By embracing the science of happiness and incorporating its principles into our daily lives, we have the potential to lead more fulfilling and meaningful existences, collectively contributing to a happier and healthier society.



 UN
UN 




