A study conducted by the World Environment Institute of the Chinese Academy of Sciences with international researchers has found that the asymmetric melting of ice sheets between the North and South Poles is linked to climate change.
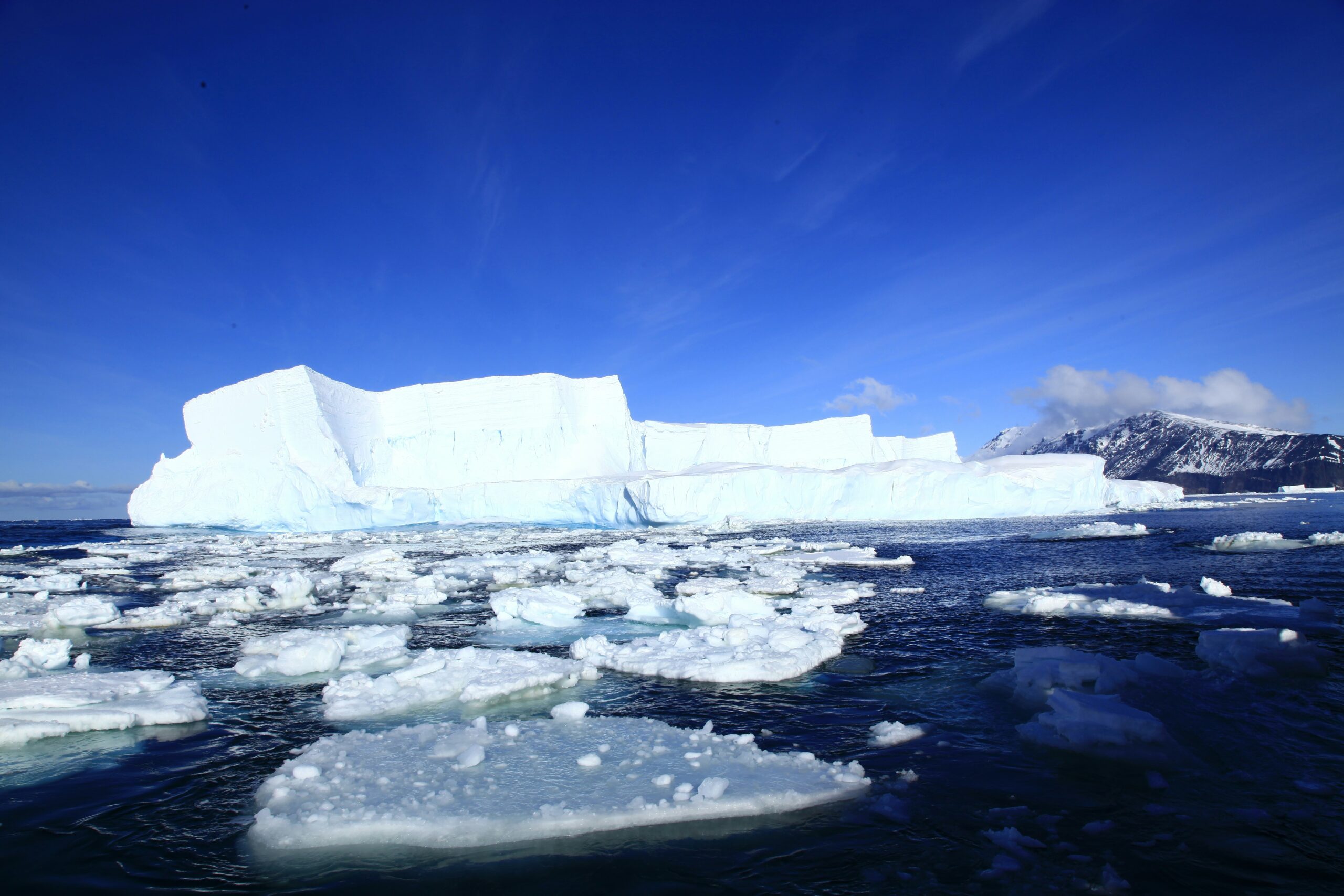
According to the study, the Antarctic ice sheets in the southern hemisphere experienced significant growth between 1.25 million and 2 million years ago. As the ice sheets grew, the sea ice in the Southern Ocean expanded. This expansion caused the northern latitudes to cool and the ice to grow in the northern hemisphere.
An Zhisheng of the Chinese Academy of Sciences said that the asymmetric melting between the ice sheets is caused by climate change and emphasized that the research is important in assessing this relationship. Zhisheng noted that glaciers in the Northern Hemisphere and the Arctic Ocean are melting rapidly, while glacial masses in Antarctica are melting relatively more slowly.
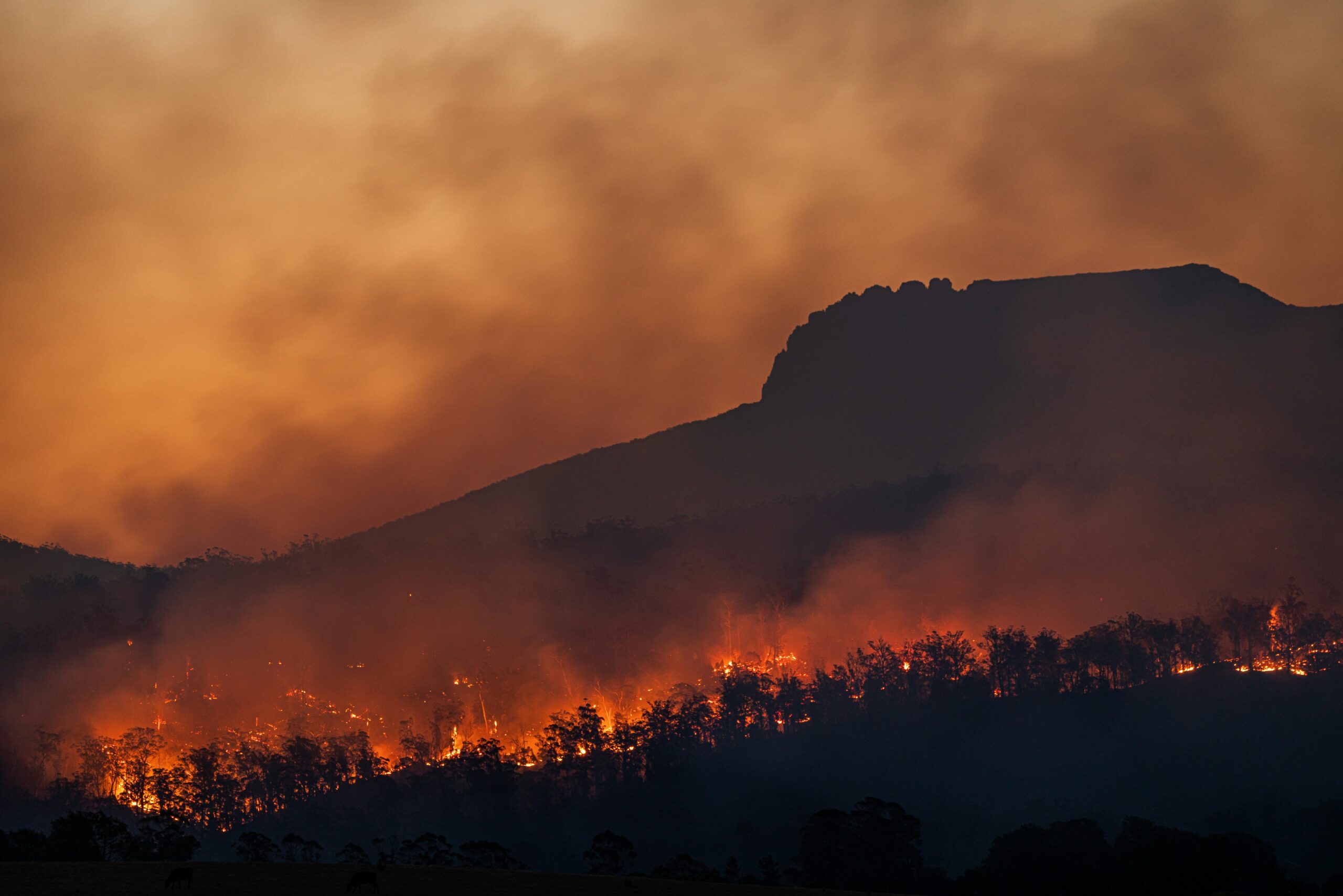
The study attributed the slower melting of glaciers in Antarctica to the presence of colder and more stable climatic conditions in the region. In contrast, the rapid melting of glaciers in the Arctic Ocean was attributed to warmer and more variable climatic conditions in the northern hemisphere. This asymmetric melting creates an imbalance in heat distribution between the poles, further complicating the global climate system.
An Zhisheng said the dynamics between the growth and shrinkage of ice sheets is critical to improving the accuracy of climate change models. “This study will help us better understand the impact of climate change on glaciers in the polar regions and enable us to make more accurate predictions for future climate change scenarios,” Zhisheng said.
The study’s findings once again underscore the importance of global cooperation in the fight against climate change. The scientists pointed out that the melting of polar ice could have far-reaching consequences, such as sea level rise, changes in weather patterns, and impacts on ecosystems. Therefore, more efforts are needed to mitigate the effects of global warming.
Details of the research have been published in the journal Science. The study is considered an important step forward in the field of climate science and lays the foundation for future research.
Source: AA



 UN
UN 




