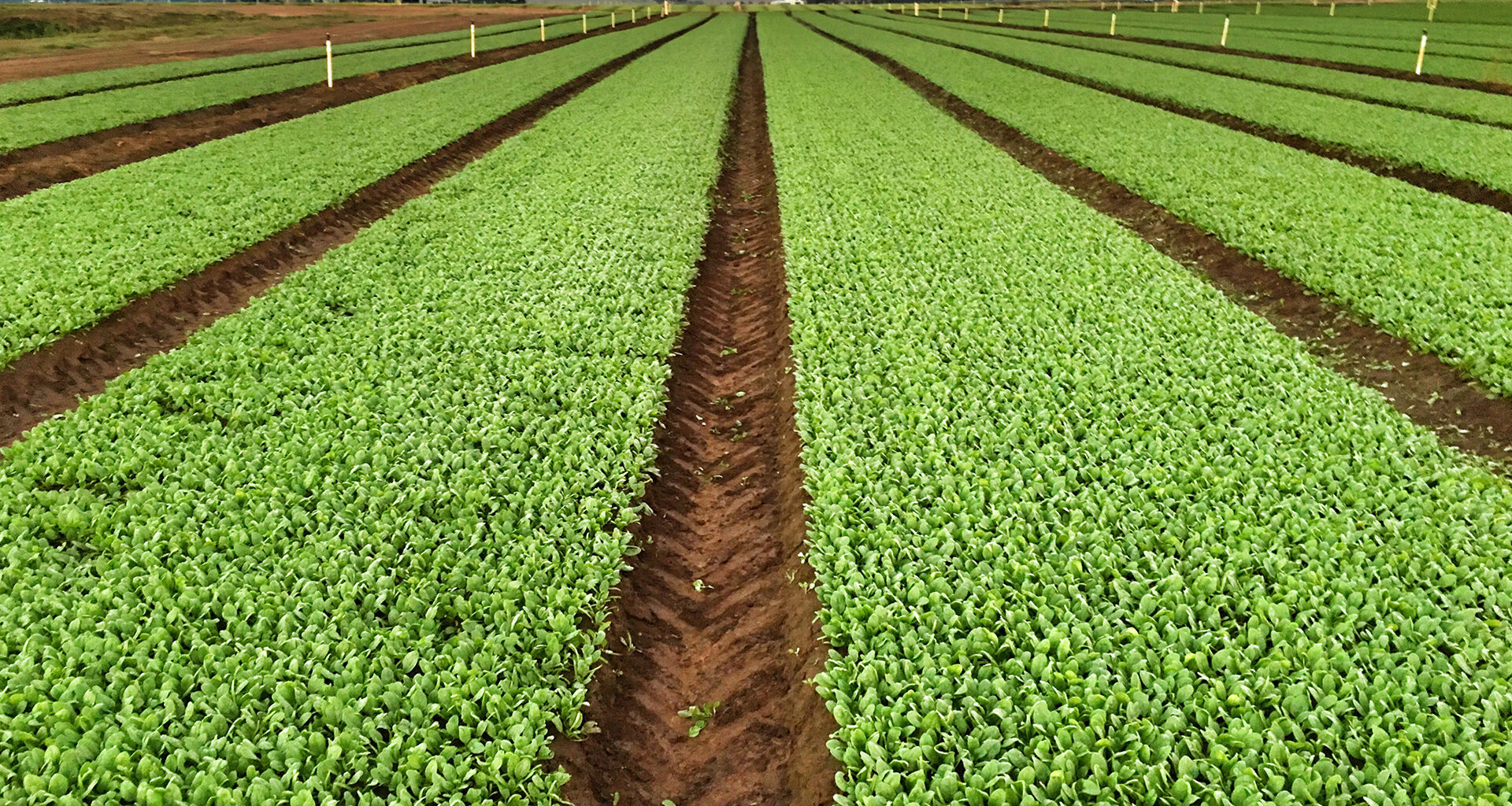
In a promising turn of events, global hunger rates have experienced a remarkable decline in recent years, thanks to the widespread adoption of sustainable farming practices. This positive trend reflects a significant step toward achieving the United Nations’ Sustainable Development Goal of zero hunger and highlights the transformative power of sustainable agriculture.
The Challenge of Global Hunger: For decades, global hunger has been a persistent challenge, with millions of people facing food insecurity and malnutrition. Factors such as extreme weather events, conflict, poverty, and inefficient agricultural practices have contributed to this crisis. However, recent developments are bringing renewed hope.
The Rise of Sustainable Farming: Sustainable farming practices are at the heart of the positive shift in global hunger rates. These practices prioritize environmental stewardship, economic viability, and social equity while producing nutritious and abundant food. Some key components of sustainable farming include:
- Regenerative Agriculture: This approach focuses on restoring and enhancing soil health, which not only improves crop yields but also sequesters carbon and increases the resilience of farms to climate change.
- Crop Diversity: Diversifying crops and adopting agroecological practices reduce the risk of crop failure, enhance nutrition, and support biodiversity.
- Reduced Food Waste: Efforts to reduce food waste in the supply chain and at the consumer level ensure that more food reaches those in need.
- Support for Smallholders: Empowering small-scale farmers with access to resources, knowledge, and markets is crucial for enhancing food security.
Success Stories: Several regions around the world have experienced significant improvements in food security due to sustainable farming practices:
- Sub-Saharan Africa: In countries like Ethiopia and Kenya, the adoption of agroecological practices has led to increased crop yields, reduced soil degradation, and improved food security for rural communities.
- Asia: Sustainable rice farming practices, such as the System of Rice Intensification (SRI), have contributed to higher rice yields and improved livelihoods for smallholders in countries like India and Cambodia.
- Latin America: Agroforestry and integrated farming systems have helped combat deforestation, increase biodiversity, and improve food security in countries like Brazil and Costa Rica.
Global Collaboration and Investment: The reduction in global hunger rates underscores the importance of international collaboration, investment, and policy support for sustainable agriculture. Governments, NGOs, and international organizations are working together to promote sustainable farming practices, provide training to farmers, and ensure access to markets for their produce.
Challenges Ahead: While the progress is promising, challenges remain. Climate change poses a significant threat to agriculture, and efforts to adapt to changing conditions must continue. Additionally, equitable access to resources, land tenure rights for smallholders, and addressing food distribution inequalities are critical aspects of the fight against hunger.
A Path Forward: The decline in global hunger rates serves as a testament to the transformative potential of sustainable farming practices. By prioritizing the health of the planet, fostering resilient agricultural systems, and supporting small-scale farmers, the world is moving closer to achieving the goal of zero hunger. Continued efforts in sustainable agriculture can pave the way for a future where everyone has access to sufficient, nutritious food, ultimately improving the well-being of communities worldwide.



 UN
UN 


