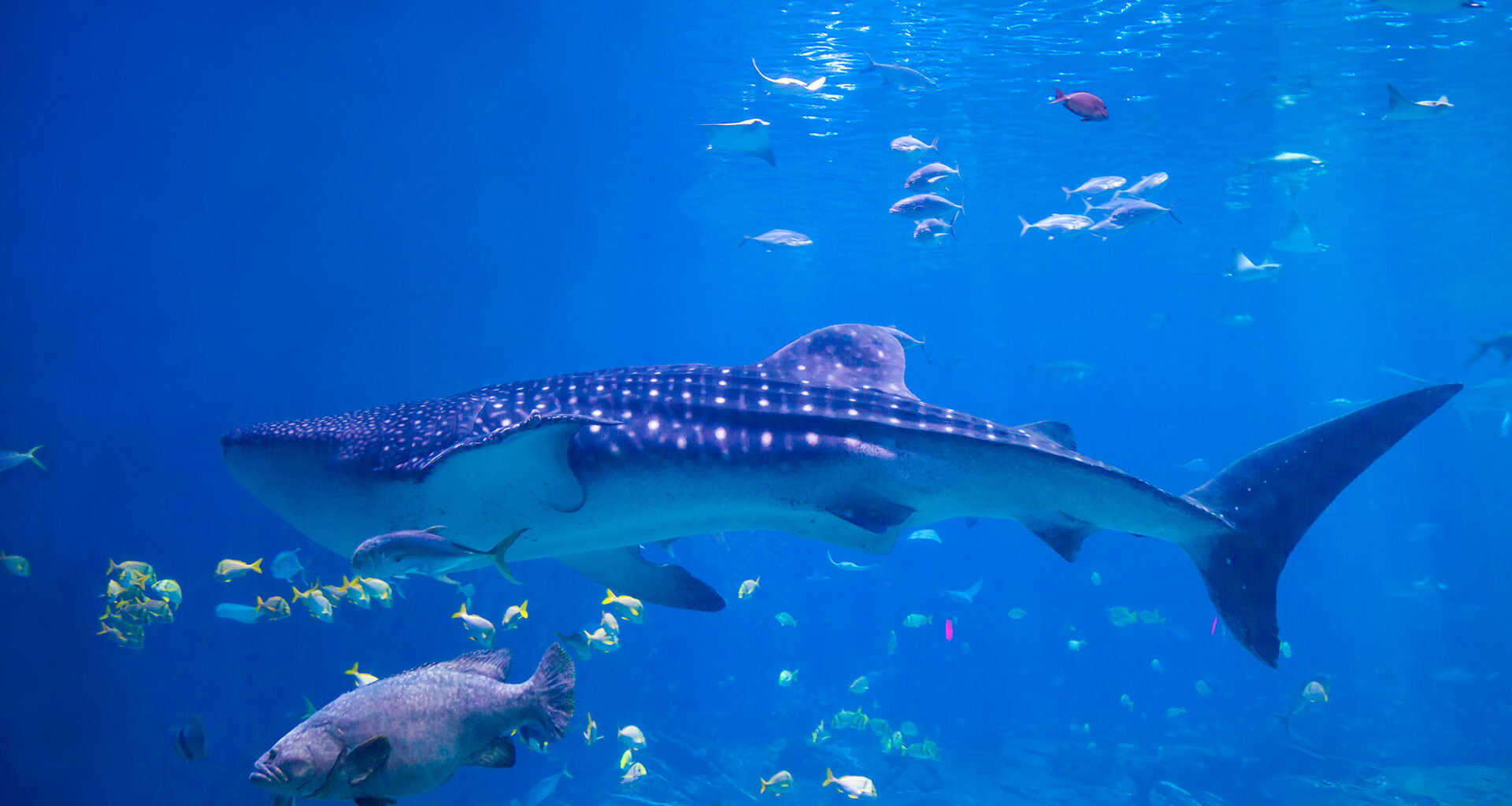
Biodiversity, the rich tapestry of life on Earth, is under unprecedented threat from human activities. Deforestation, habitat destruction, pollution, and climate change are driving countless species toward extinction. To counter this crisis and protect the planet’s remarkable diversity of life, a global initiative has emerged, uniting nations, organizations, and individuals in a collective effort to safeguard threatened species and conserve our natural heritage.
The Biodiversity Crisis:
The loss of biodiversity is an urgent global concern with profound implications for ecosystems and human well-being. This crisis is driven by several interconnected factors:
- Habitat Loss: The conversion of natural habitats into agriculture, urban areas, and infrastructure fragments ecosystems, disrupts migration patterns, and threatens countless species.
- Climate Change: Rising temperatures and changing weather patterns affect the distribution and behavior of species, often pushing them toward extinction.
- Pollution: Contaminants from agriculture, industry, and plastic waste in oceans pose a direct threat to many species and disrupt ecosystems.
- Overexploitation: Unsustainable hunting, fishing, and poaching endanger numerous species, from elephants to fish populations.
- Invasive Species: The introduction of non-native species can have devastating consequences for local ecosystems and native species.
The Global Initiative to Protect Biodiversity:
In response to the biodiversity crisis, a global initiative has been launched, underpinned by several key components:
- The Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD): This international treaty, often referred to as the “Biodiversity Convention,” provides a framework for the conservation of biodiversity and the sustainable use of its components. The CBD’s objectives include the conservation of biological diversity, sustainable use of its components, and the fair and equitable sharing of benefits.
- Protected Areas: Establishing and maintaining protected areas, such as national parks and marine reserves, is critical for safeguarding ecosystems and providing safe havens for endangered species.
- Restoration and Reforestation: Efforts to restore damaged ecosystems and reforest areas contribute to both habitat restoration and carbon sequestration, helping mitigate climate change.
- Sustainable Practices: Encouraging sustainable practices in agriculture, fisheries, and forestry reduces the impact of human activities on biodiversity.
- Research and Monitoring: Ongoing research and monitoring efforts provide valuable data on species populations, distribution, and health, enabling informed conservation decisions.
Conservation Success Stories:
Conservation initiatives have already yielded success stories, including:
- Panda Conservation: Efforts to protect giant pandas in China have led to a rebound in their population, moving them from “endangered” to “vulnerable” on the IUCN Red List.
- Whale Recovery: Bans on whaling and conservation measures have contributed to the recovery of several whale species.
- Coral Restoration: Projects to restore coral reefs and combat coral bleaching are showing promise in safeguarding these vital ecosystems.
The Road Ahead:
While progress has been made, the road to biodiversity conservation remains challenging:
- Global Collaboration: Conservation efforts require international cooperation and commitments from nations worldwide.
- Policy and Regulation: Effective policies and regulations are essential to curbing habitat destruction, overexploitation, and other threats to biodiversity.
- Public Awareness: Raising awareness about the importance of biodiversity and the need for conservation is crucial in driving action at all levels of society.
- Sustainable Practices: Transitioning to sustainable practices in agriculture, fisheries, and forestry is essential for long-term biodiversity protection.
- Climate Action: Addressing climate change is intrinsically linked to biodiversity conservation, as a stable climate is essential for ecosystems and species survival.
The global initiative to protect biodiversity represents a vital response to the urgent challenges facing Earth’s diverse life forms. It is a testament to humanity’s capacity to recognize the importance of our natural world and take collective action to ensure its preservation for future generations. As we strive to safeguard threatened species and restore ecosystems, we move closer to a more harmonious coexistence with the planet’s incredible biodiversity.



 UN
UN 




