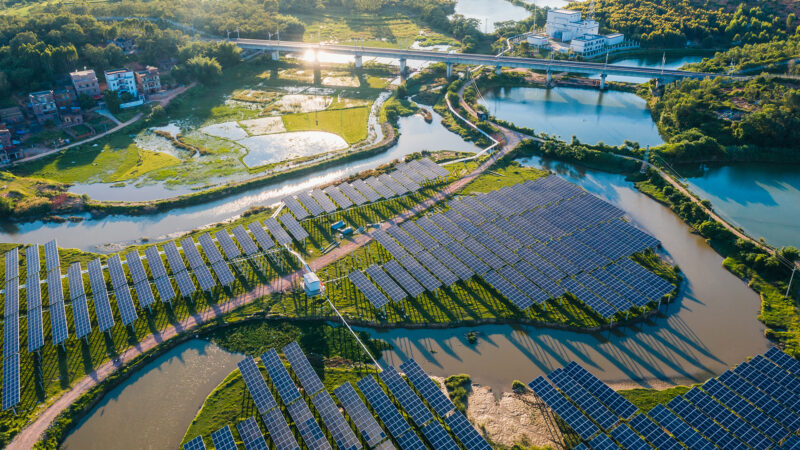
In recent years, the renewable energy sector has experienced unprecedented growth and innovation, with solar power emerging as a leading force in revolutionizing the global energy landscape. The surge in solar energy adoption is reshaping how we generate, consume, and think about power, offering a sustainable alternative to traditional fossil fuels and addressing pressing environmental concerns.
The Rise of Solar Power:
Solar power, harnessed from the sun’s energy through photovoltaic (PV) cells, has witnessed a remarkable surge in popularity for several compelling reasons:
- Clean Energy Source: Solar power is a clean, renewable energy source that generates electricity without emitting greenhouse gases or air pollutants, thus mitigating the impacts of climate change and air pollution.
- Abundant and Accessible: Solar energy is abundant and accessible almost everywhere on the planet, with varying degrees of solar irradiance making it suitable for a wide range of locations.
- Technological Advancements: Ongoing advancements in solar technology have significantly reduced costs, making it increasingly competitive with fossil fuels.
- Energy Independence: Solar power empowers individuals, communities, and nations to generate their own electricity, reducing reliance on centralized energy grids and increasing energy security.
- Job Creation: The solar industry has become a significant source of employment, offering a wide range of job opportunities from manufacturing and installation to research and development.
Transformation of the Energy Landscape:
The proliferation of solar power is driving a transformation in the energy landscape:
- Decentralization: Solar panels on rooftops, in communities, and on industrial sites contribute to a decentralized energy grid, enhancing resilience and reliability.
- Grid Integration: Advanced grid integration technologies enable the efficient incorporation of solar energy into existing power grids, reducing peak demand and enhancing grid stability.
- Energy Storage: The development of energy storage solutions, such as batteries, allows excess solar energy to be stored and used during cloudy days or at night, increasing reliability.
- Electrification: Solar power is powering the electrification of transportation and heating, reducing reliance on fossil fuels in these sectors.
Environmental Impact:
The environmental benefits of solar power are significant:
- Reduced Emissions: Solar power displaces the need for fossil fuels, reducing carbon dioxide emissions and air pollution, which has direct public health benefits.
- Conservation of Resources: Solar power reduces the demand for finite resources like coal, oil, and natural gas.
- Biodiversity Preservation: By mitigating climate change, solar power contributes to the preservation of ecosystems and biodiversity.
Global Initiatives and Success Stories:
Countries and regions around the world are investing in solar power:
- Germany: Germany’s “Energiewende” policy promotes the transition to renewable energy, with solar power playing a significant role.
- China: China is the world’s largest producer and consumer of solar panels, with ambitious plans to expand its solar capacity.
- California: California has set ambitious renewable energy targets and is a leader in residential solar installations.
Challenges and Considerations:
Despite its rapid growth, solar power faces challenges, including intermittency (solar power generation depends on sunlight), land use concerns, and the need for infrastructure updates.
A Sustainable Future:
Solar power’s surge marks a pivotal moment in the global transition toward a sustainable and clean energy future. As technology advances, costs continue to decline, and governments, businesses, and individuals embrace solar energy, it has the potential to power not only our homes and industries but also our aspirations for a cleaner, greener planet. The solar revolution represents a beacon of hope for addressing climate change and building a sustainable world for future generations.



 UN
UN 


