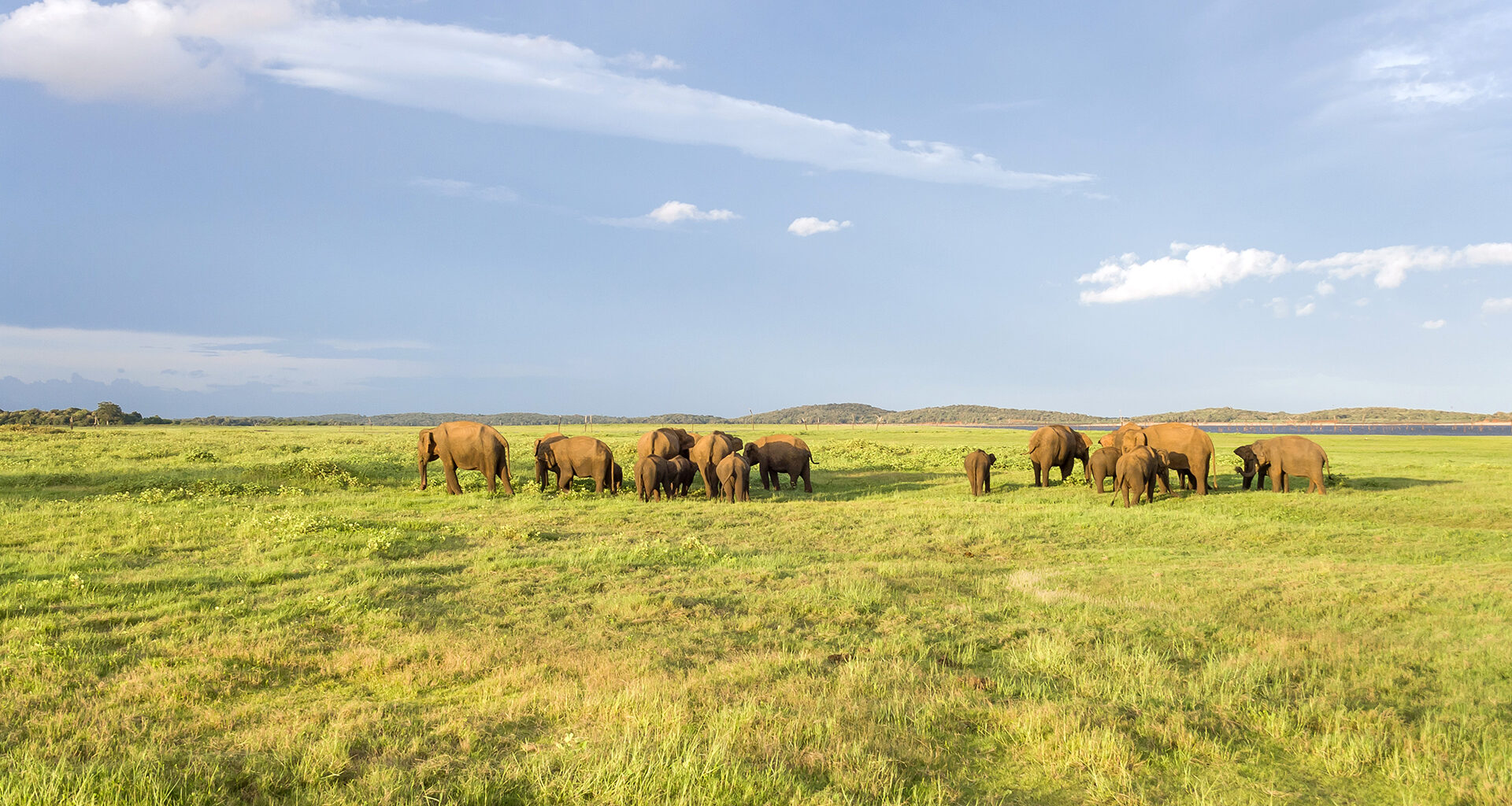
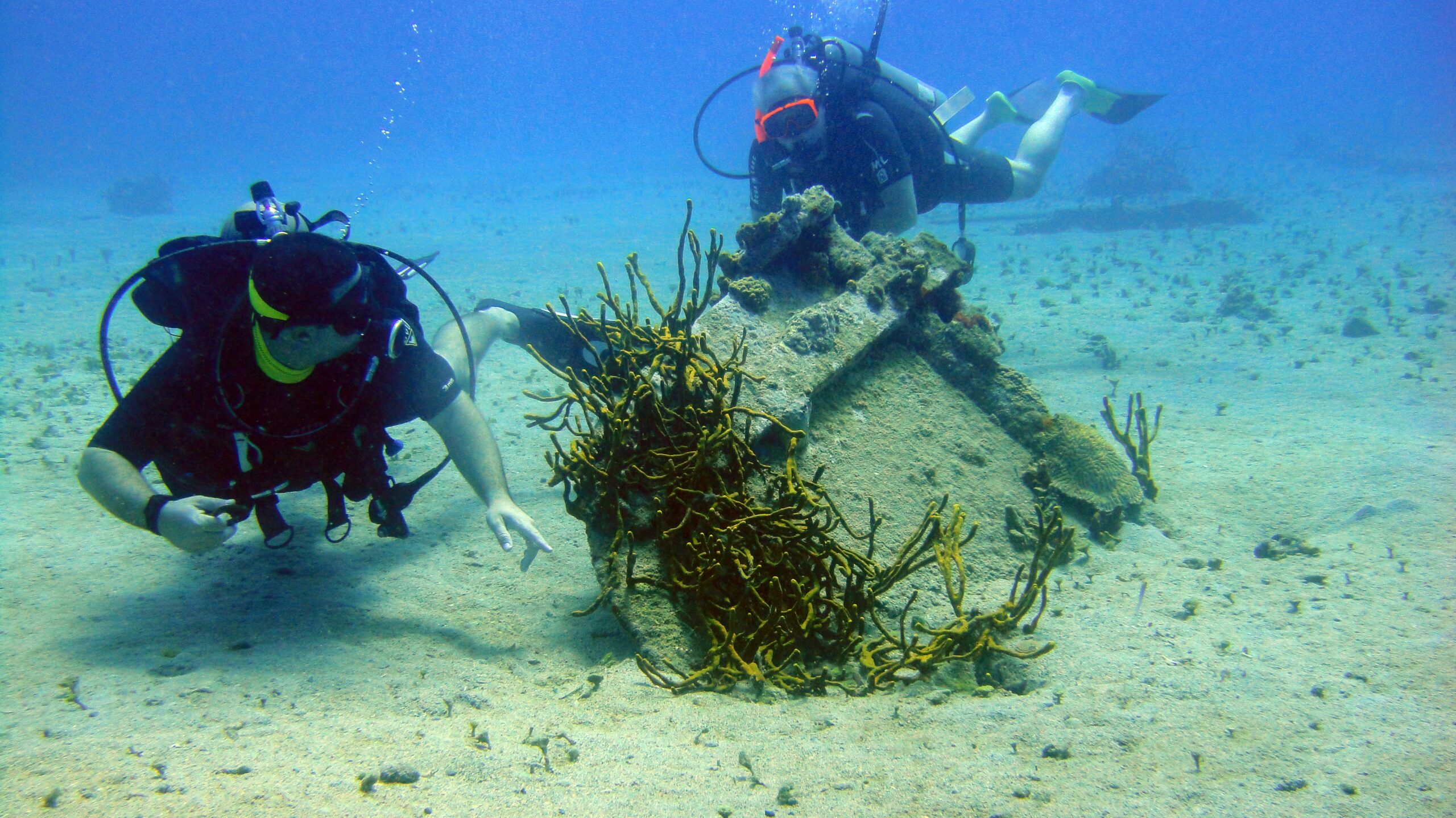
Around the world, biodiversity and wildlife face unprecedented threats from habitat loss, climate change, poaching, and other human activities. In response to these challenges, nations are increasingly recognizing the urgent need to protect terrestrial and marine habitats. Commitments to conservation and the establishment of protected areas represent a global effort to safeguard Earth’s diverse ecosystems and the species that call them home.
The Importance of Habitat Preservation:
Preserving habitats is crucial for several reasons:
- Biodiversity: Habitats are home to a wide range of plant and animal species, and preserving them ensures the survival of diverse ecosystems.
- Ecosystem Services: Natural habitats provide essential ecosystem services such as clean air and water, pollination, and climate regulation.
- Climate Change Mitigation: Healthy habitats, like forests and wetlands, sequester carbon and play a critical role in mitigating climate change.
- Human Well-Being: Many communities depend on healthy habitats for their livelihoods and cultural heritage.
Global Commitments to Conservation:
Nations are taking various measures to protect habitats:
- Protected Areas: Countries are designating and expanding protected areas, parks, and reserves to safeguard critical habitats and wildlife.
- International Agreements: Global initiatives like the Convention on Biological Diversity and the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals include commitments to habitat conservation.
- Conservation Financing: Many countries and international organizations are investing in conservation programs and supporting sustainable land and ocean management.
- Indigenous Stewardship: Recognizing the role of Indigenous communities as custodians of vital habitats, nations are working to strengthen Indigenous land rights and partnerships in conservation efforts.
Terrestrial Habitat Preservation:
- Forests: Protecting forests helps conserve biodiversity, store carbon, and prevent deforestation.
- Wetlands: Preserving wetlands is critical for water purification, flood control, and habitat for many species.
- Grasslands and Savannas: These habitats are home to diverse wildlife, including large herbivores and predators.
Marine Habitat Preservation:
- Coral Reefs: Efforts to protect coral reefs focus on reducing pollution, overfishing, and rising sea temperatures.
- Marine Protected Areas: Establishing marine protected areas helps safeguard marine ecosystems, including seagrass beds, kelp forests, and open ocean habitats.
Success Stories:
- Galápagos Islands, Ecuador: The Galápagos Marine Reserve and National Park are renowned for their unique biodiversity and strict conservation measures.
- Yellowstone National Park, USA: Yellowstone is a symbol of successful terrestrial habitat conservation and wildlife preservation.
Challenges and Considerations:
- Enforcement: Effective enforcement of conservation measures remains a challenge, particularly in regions with limited resources.
- Human-Wildlife Conflict: Balancing habitat protection with the needs of local communities and mitigating human-wildlife conflicts is complex.
- Climate Change: Climate change poses a significant threat to habitats and requires adaptive conservation strategies.
A Path to a Sustainable Future:
Preserving terrestrial and marine habitats is a fundamental step toward ensuring a sustainable future for all life on Earth. As nations commit to conservation efforts and take action to protect critical ecosystems, they contribute to the preservation of biodiversity, climate mitigation, and the well-being of present and future generations. It is a collective endeavor that requires international cooperation, innovative conservation strategies, and a deep commitment to safeguarding our planet’s natural wonders.



 UN
UN 


